October 2 is Manufacturing Day, a national celebration of modern manufacturing.
In honor of the special day, we’re sharing an illustrative “How It Works” guide that offers a step-by-step look at the cold root rolling process and how it prolongs the life of drilling equipment in the oil and gas industry.
Here’s how it works.
Step 1: Installation
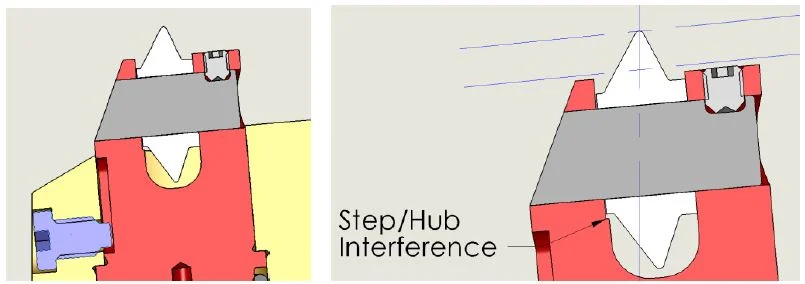
CJWinter has developed specialized tools to roll both pin and box connections, and they’re compatible with virtually all controls — including popular lathes and controls like Fanuc, Weiler, and Mazak. It doesn’t require an external power device or accumulator, and loads easily on the control with an Error Proof Loading System.
The EPL system uses an asymmetric hub system where the hub on one side of the roll is larger than the other. The hubs work in conjuntion with a step in the roll holder to create Step/Hub interference if the user tries to load the roll backwards.

Step 2: Burnishing
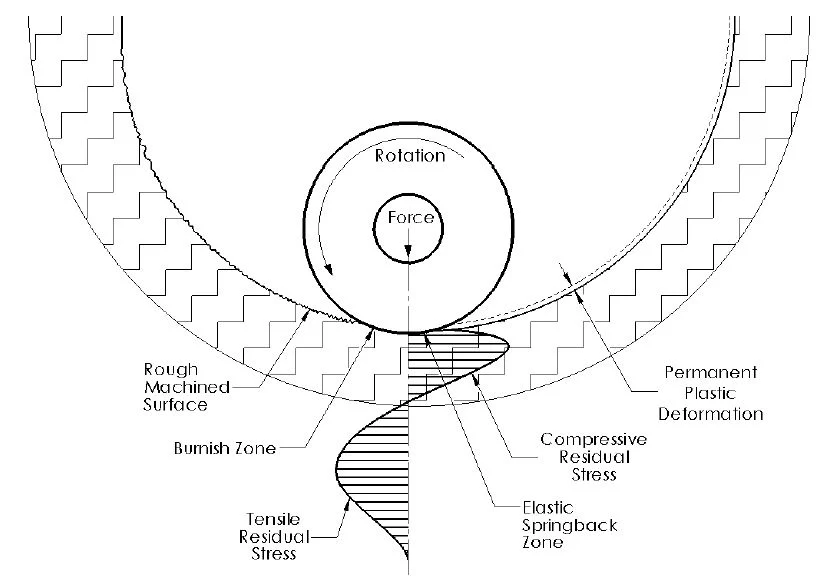
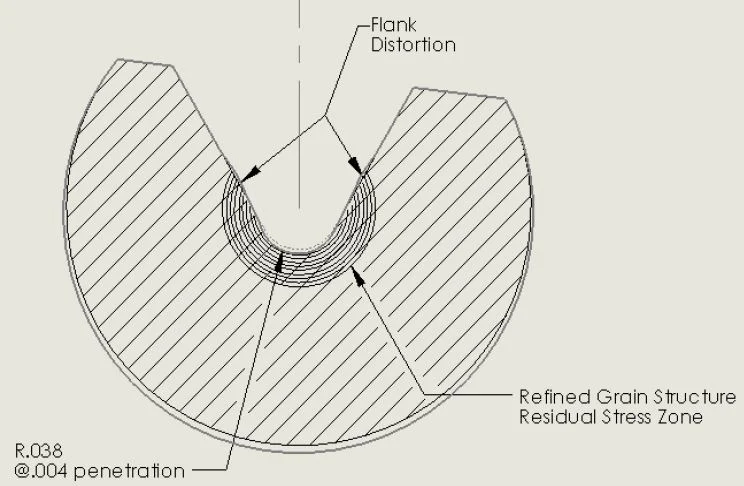
The purpose of cold root rolling is to strengthen connections. The tool works by burnishing the root radius of previously cut threads. Its hardened roll applies force to the surface of the already tapered thread.
Step 3: Cold Forming
The tool penetrates into the metal surface, which displaces the thread material and restructures the crystalline lattice of the steel grain structure. The now cold-formed material is thus more resistant to further deformation, which improves the surface finish and the strength of the root substance.
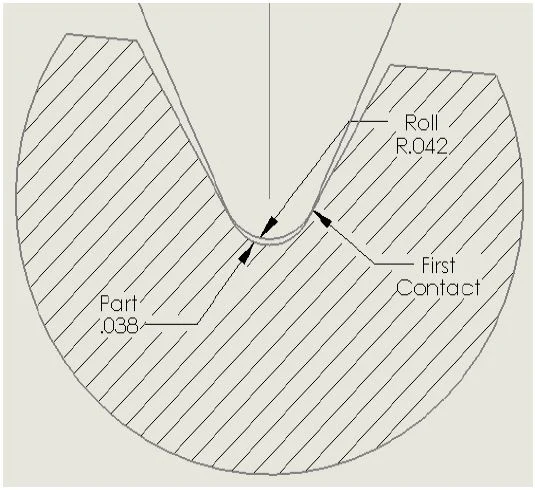
Results: Connection with Improved Stress Balance
After being cold root rolled, the rotary shouldered connection displays specific improvements in strength and stress balance.
- The residual compressive stress of cold root rolling offsets the tensile stress of service in the critical stress region of a thread root.
- The cold formed surface is more uniform, with fewer scratches, fatigue points and opportunity for chemical exposure.
- The work-hardening effect of cold root rolling discourages shallow cracking in favor of deep, short cracking that can be more easily repaired.
To learn more about cold root rolling and our tools at CJWinter, download our Informational Guide or contact the team today.